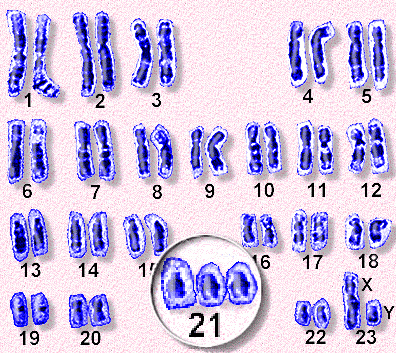
Down Syndrome
2n + 1 (chromosome 21)

Note:
i. Where the chromosomes are either
1. haploid (23)
2. Diploid (46)
3. Triploid (69)
4. Tetraploid
Q. Why couldn’t a tetraploid situation occur in humans? (4N)
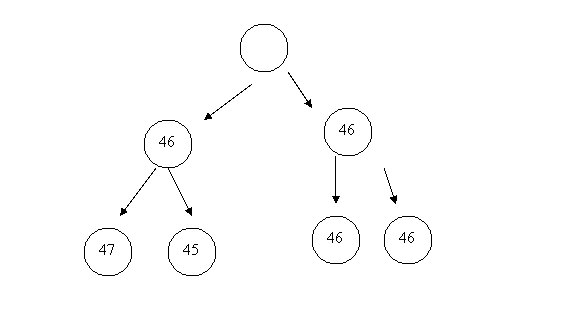
i. Abnormal chromosome number (too few or too many)
1. Monosomy (2N-1)
2. Trisomy (2N+1)
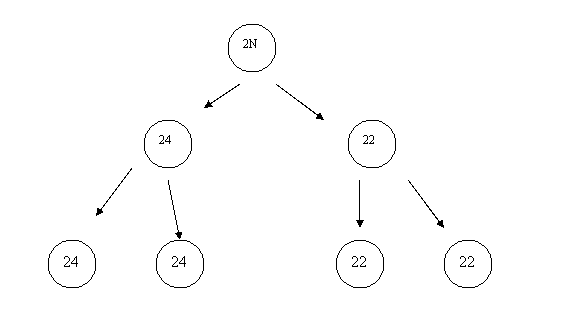
2N + 1 2N – 1
Most fetuses that have an abnormal chromosome number are aborted
3 Ways to get Down Syndrome
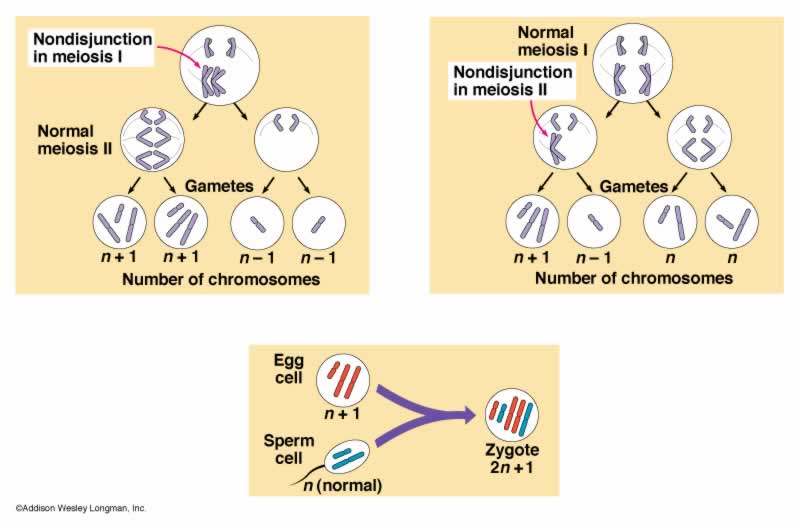
Q. What was one possible explanation as to why chromosomes become sticky?

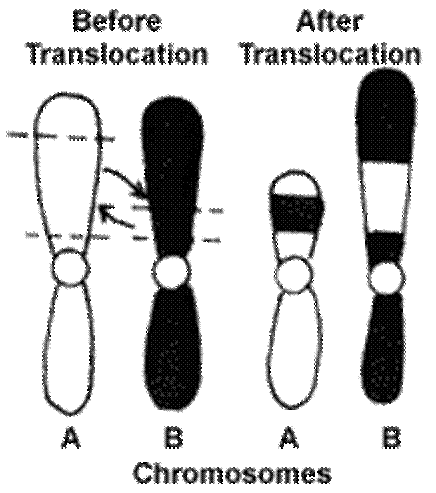
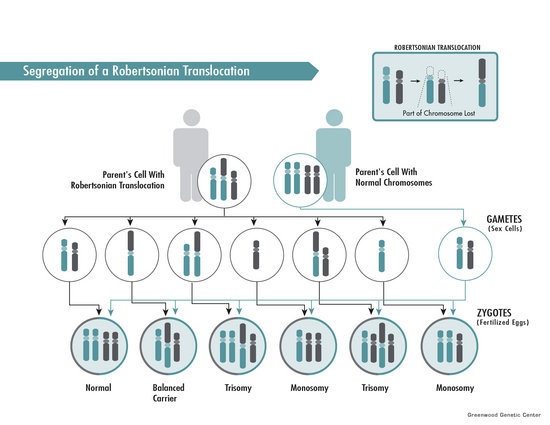
What is
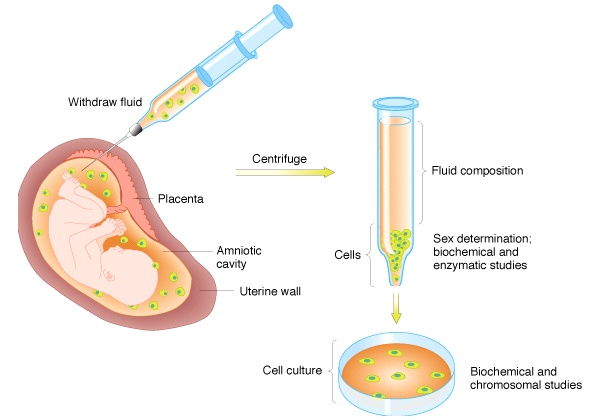
amniocentesis?
Amniocentesis is a prenatal test that allows you and your practitioner to gather
information about your baby's health and development from a sample of your
amniotic fluid. (This is the fluid that surrounds the baby in your uterus.) The
test is most commonly done when a woman is between 15 and 18 weeks pregnant to
determine whether the baby has genetic or chromosomal abnormalities, such as
Down syndrome. But not all women choose to have this test because it carries
a small risk of miscarriage.
Other reasons that you may need to have amniocentesis include:
• To check on the well being of your baby if you have a blood sensitization, such as Rh sensitization. This is a complex condition that may occur if your blood is a different type than your baby's.
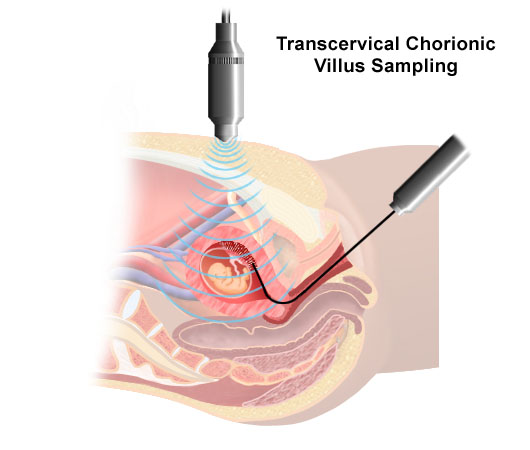
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
![]()
Chorionic
villus sampling (CVS) is a prenatal test that involves taking a tiny tissue
sample from outside the sac where the fetus develops. The tissue is tested to
diagnose or rule out certain birth defects. The test generally is performed
between 10 and 12 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period.
CVS may be offered when there is an increased risk of chromosomal or genetic
birth defects, and parents would like test results as early in pregnancy as
possible. Another prenatal test called amniocentesis can diagnose the same birth
defects, but is performed a little later in pregnancy, usually between 15 and 18
weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period.
Who is offered CVS?
CVS is not routinely offered to all pregnant women because the test carries a
small risk of miscarriage, and possibly other complications.
Fetal Cell Sorting
|
||||||
Staining
Certain chemical treatments of mammalian chromosomes yield differentially stained regions on chromosomes. The patterns obtained depend on the treatment used.